Elastic and Inelastic Collisions
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Collisions, Inelastic Collision, Linear Impulse and Coefficient of Restitution & Collision and Vertical Circular Motion etc.
Important Questions on Elastic and Inelastic Collisions
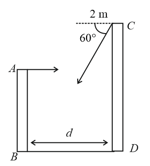
Two towers and are situated a distance apart as shown in figure. is high and is high from the ground. An object of mass is thrown from the top of horizontally with a velocity of towards . Simultaneously another object of mass is thrown from the top of at an angle of to the horizontal towards with the same magnitude of initial velocity as that of the first object. The two objects move in the same vertical plane, collide in mid-air and stick to each other. Find the position where the objects hit the ground (from ).
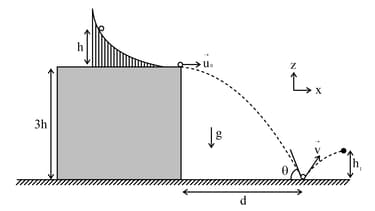
A slide with a frictionless curved surface, which becomes horizontal at its lower end, is fixed on the terrace of a building of height from the ground, as shown in the figure. A spherical ball of mass is released on the slide from rest at a height from the top of the terrace. The ball leaves the slide with a velocity and falls on the ground at a distance from the building making an angle with the horizontal. It bounces off with a velocity and reaches a maximum height . The acceleration due to gravity is and the coefficient of restitution of the ground is . Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
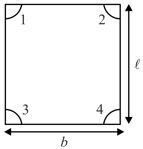
Ball is at rest somewhere on a smooth billiards table . An identical ball is moving with velocity , collides with ball A elastically. After sec both the balls simultaneously fall into pockets marked and . Find area of the table in .
There are five small elastic balls placed at rest on a smooth horizontal surface along a line. The masses of the balls are and respectively. A velocity '' is imparted to the first ball of mass and it collides with second ball, second ball collides with third and so on. The fifth ball after collision is just able to complete a vertical circular motion on a smooth circular track of radius . Find the value of '' in to nearest integer. Assume all collisions to be perfectly elastic and head on. (Take )
Imagine a gravity free space consisting of tiny particles moving horizontally at speed from both left and right. A uniform cylindrical body with its axis of symmetry parallel to the direction of motion of particles is released from rest as shown
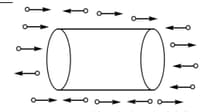
The particles bombard the body uniformly from both left and right. Collision of particles with the right end of the cylinder is perfectly elastic while those with the left are perfectly inelastic, though the particles do not stick to the cylinder after the collision. Neglect the heat produced during collision. Mark the correct statements.
A ball of mass moving horizontally at a speed collides with the bob of a simple pendulum at rest. The mass of the bob is also . Here . (Where is length of the pendulum)
A ball moving horizontally collides with a uniform rod which is free to rotate in the vertical plane about horizontal axis passing through its upper end . Collision is instantaneous and inelastic. For this collision, which of the following statements are not correct immediately after collision for the system of ball and rod?
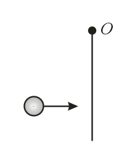
Two bodies and B of masses and moving in free space in opposite directions with velocities and respectively undergo a head-on collision. The force of their mutual interaction varies with time according to the given graph. What can you conclude from the given information?
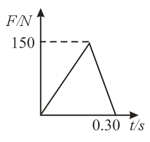
A vertical spring of spring constant is compressed by by a block of mass as shown in figure. Block is released from rest. Spring can be gently detached from block at any moment. At the instant of detachment, a particle of mass moving with speed horizontally collides with the block perfectly inelastically.
A sphere of mass collides elastically with another stationary sphere of mass obliquely. Both the spheres are smooth and there are no external forces acting on them. Maximum angle through which sphere of mass can be deflected w.r.t. Its initial direction of motion is . Value of is
A ball with initial speed of collides elastically with two other identical ball whose centres are on a line perpendicular to the initial velocity and which are initially in contact with each other. All the three ball are lying on a smooth horizontal table. The first ball is aimed directly at the contact point of the other two balls. All the balls are smooth. Find the velocities of the three balls after the collision:
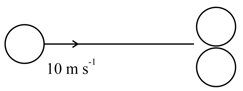
Two identical balls are kept on smooth ground as shown. The left ball is projected towards right ball. The collision between balls and between ball and wall are elastic. Which of the following scenario(s) are possible in subsequent motion?
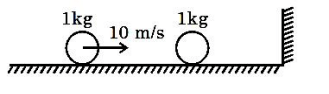
A ball of mass moving with a speed of on a smooth horizontal plane collides obliquely with another ball of same mass at rest as shown in fig. If coefficient of restitution for the collision is , the speed of the striking ball after collision is _____
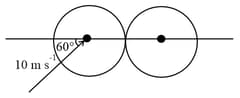
Two boards have been placed at right angles to one another. Their line of touching is horizontal. An elastic ball is released at a point at a point at distance a from the plane and from . On the average, how many times does the ball bounce against wall for each time it bounces against wall ? Collises are absolutely elastic.
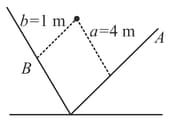
A point of mass collides elastically with a stationary point mass of . After their collision, the mass reverses its direction and moves with a speed of . Which of the following statements(s) is/are correct for the system of these two masses?
A small block of mass moves on a frictionless surface of an inclined plane, as shown in the figure. The angle of the incline suddenly changes from to at point B. The block is initially at rest at A. Assume that collisions between the block and incline are totally inelastic. . 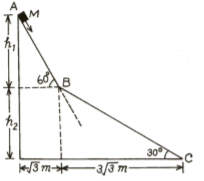
A block of mass is moving with a speed of on a smooth surface. It strikes another mass of and then they move together as a single body. The energy loss during the collision is:
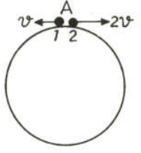
Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite directions from a point in a horizontal circular orbit. Their tangential velocities are and , respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move with constant speeds. After making how many collisions, other than that at , these two particles will again reach the point ?
A smooth sphere is moving on a frictionless horizontal plane with angular speed and centre-of- mass velocity . It collides elastically and head-on with an identical sphere at rest. Neglect friction everywhere. After collision, their angular speeds are and respectively. Then:
Consider a rubber ball freely falling from a high height on to a horizontal elastic plate. Assume that the duration of collision is negligible and the collision with the plate is totally elastic. Then the velocity as a function of time and the height as a function of time will be:
